Discovering The Value Of A Quart: An In-Depth Exploration
When it comes to understanding measurements, especially in cooking and everyday life, knowing how much is a quart can make all the difference. The quart is a unit of volume that is used predominantly in the United States and a few other countries that have not fully adopted the metric system. Despite its seemingly straightforward nature, the quart can sometimes be a source of confusion, particularly for those who are more accustomed to metric measurements. This article aims to unravel the intricacies of the quart, exploring its history, conversions, and practical applications, to provide a comprehensive understanding of this essential unit of measurement.
The quart has a rich history that traces back to ancient times when measurements were less standardized than today. Over the centuries, the quart has evolved, taking on different definitions depending on the region and context. This evolution reflects not only changes in society and technology but also the enduring need for a convenient and understandable way to measure volume. As we delve into the world of quarts, we will explore how this unit fits into the broader system of measurements, providing both historical context and practical examples.
Understanding how much is a quart is not only crucial for those living in regions that use the Imperial or US customary systems but also for anyone engaged in international cooking, trade, or scientific endeavors. By examining the quart from various angles, including its conversions to other units and its role in different fields, we will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate this aspect of measurement. Whether you're a student, a professional, or a curious learner, this article will serve as a valuable resource in your quest to master the quart.
Table of Contents
- History of the Quart
- Understanding the Quart
- Quart in Different Measurement Systems
- Converting Quarts to Other Units
- Quart in Cooking and Baking
- Quart in Scientific Research
- Quart in International Trade
- Common Misconceptions About Quarts
- Tools for Measuring Quarts
- The Future of the Quart
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
History of the Quart
The history of the quart is a journey through time, showcasing the evolution of measurement systems and the human need for standardization. The quart, as we know it today, has its origins in the medieval British system of measurement. During this period, measurements were often based on physical objects or natural phenomena, leading to a variety of units with the same name but different values.
In medieval England, the quart was part of the wine and ale measurements, which were integral to trade and daily life. The word "quart" is derived from the Latin "quartus," meaning "fourth part," which indicates its relation to the gallon. However, the exact volume of a quart could vary significantly depending on the substance being measured and the region.
As trade expanded and societies became more interconnected, the need for standardized measurements became apparent. The British Imperial System, established in 1824, aimed to unify these disparate units into a coherent system. The imperial quart was defined as equal to one-fourth of an imperial gallon, which is approximately 1.136 liters. This standardization made it easier to trade goods and services across different regions and countries.
In the United States, the customary system evolved from the British system but diverged at various points. The US liquid quart is slightly smaller than the imperial quart, equal to 32 fluid ounces or approximately 0.946 liters. This difference between the US and the UK systems can still lead to confusion today, but it also reflects the unique historical paths these systems have taken.
The history of the quart is not just a story of numbers and conversions; it is a testament to the evolving nature of human societies and their need to adapt and standardize for progress. Understanding this history provides a foundation for appreciating the quart's role in contemporary measurement systems.
Understanding the Quart
To fully grasp how much is a quart, it's essential to understand what a quart represents in practical terms. A quart is a unit of volume used to measure liquids and dry goods. In the US customary system, one quart is equal to 32 US fluid ounces, 2 pints, or 4 cups. When measuring dry goods, the quart is still used, although the measurements can slightly differ due to the nature of the substances being measured.
The quart is often used in everyday contexts, such as measuring milk, juice, or other beverages. It is also a common unit in recipes, especially in countries like the United States that rely heavily on the customary system. Knowing how much is a quart can help in accurately following recipes and ensuring the right proportions in cooking and baking.
In addition to its practical uses, the quart is also an important educational tool. Learning about quarts and their conversions to other units helps students develop a better understanding of volume and measurement concepts. This understanding is crucial for success in various academic disciplines, including mathematics, science, and engineering.
Moreover, as a unit of measurement, the quart plays a vital role in industries ranging from agriculture to manufacturing. Accurate measurement is essential for maintaining quality control, ensuring product consistency, and optimizing processes. The quart, with its historical significance and practical applications, remains a cornerstone of measurement in these fields.
Quart in Different Measurement Systems
The quart exists in several measurement systems, each with its own definition and applications. The two most common systems that use the quart are the US customary system and the British Imperial system. Understanding the differences between these systems is crucial for anyone working or studying in fields that require precise measurements.
In the US customary system, the quart is a unit of liquid volume equal to 32 US fluid ounces, 2 pints, or 4 cups. It is commonly used in cooking, grocery shopping, and other everyday activities. The US dry quart is slightly different, used primarily for measuring dry ingredients, and is equivalent to 67.2 cubic inches or approximately 1.101 liters.
The British Imperial system, on the other hand, defines the quart as equal to 40 imperial fluid ounces or approximately 1.136 liters. This difference in volume between the US and UK quarts can lead to confusion, especially in international contexts. However, it also highlights the historical divergence of measurement systems and the continued coexistence of different standards.
In addition to these systems, the quart is sometimes used in the metric system, although it is not an official metric unit. In countries that have adopted the metric system, the quart is often replaced by liters and milliliters. However, the quart may still appear in certain contexts, especially in international trade and cultural exchanges.
Understanding the quart's role in different measurement systems is essential for navigating a world where multiple standards coexist. This knowledge allows for accurate conversions, better communication, and a deeper appreciation of the complexity and diversity of measurement systems worldwide.
Converting Quarts to Other Units
One of the most common questions regarding how much is a quart involves its conversion to other units of measurement. Whether you're working with recipes, scientific data, or international trade, knowing how to convert quarts to other units is a valuable skill.
In the US customary system, one liquid quart is equivalent to 32 US fluid ounces, 2 pints, or 4 cups. For those using the metric system, one US quart is approximately equal to 0.946 liters. This conversion is essential for those involved in activities that require precise measurements, such as cooking, baking, and scientific research.
When converting quarts to smaller units, such as fluid ounces or cups, it's important to remember that these conversions are based on the US customary system. In the UK, the imperial quart is larger and is equal to 40 imperial fluid ounces or approximately 1.136 liters. This difference means that conversions between the US and UK systems require attention to detail and careful calculation.
For dry goods, the US dry quart is used, which is slightly larger than the liquid quart. One US dry quart is equivalent to 67.2 cubic inches or approximately 1.101 liters. This conversion is particularly important in agriculture and food production, where accurate measurement of dry ingredients is crucial for quality control and consistency.
To convert quarts to other units, you can use conversion tables, online calculators, or mathematical formulas. Understanding these conversions allows for accurate measurement and communication across different systems, ensuring that you can confidently work with quarts in any context.
Quart in Cooking and Baking
In the culinary world, understanding how much is a quart is essential for both amateur cooks and professional chefs. The quart is a common unit of measurement in recipes, especially those originating from the United States, and plays a vital role in ensuring the correct proportions of ingredients.
When following a recipe, accurate measurement of liquids is crucial for achieving the desired taste and texture. A quart is often used to measure liquids like water, milk, and broth, which are foundational ingredients in many dishes. For dry ingredients, the quart can also be used, although it is more common to see measurements in cups or grams, especially in baking.
Baking, in particular, requires precision and consistency, as the balance of dry and wet ingredients can significantly affect the outcome. Understanding how much is a quart allows bakers to convert recipes accurately, especially when scaling them up or down. For example, if a recipe calls for 2 quarts of liquid, knowing that this is equivalent to 8 cups can help in adjusting the quantity as needed.
For those who enjoy experimenting in the kitchen, understanding quarts and their conversions to other units can open up a world of possibilities. By confidently working with quarts, cooks can adapt recipes from different countries, combining flavors and techniques from various culinary traditions.
In addition to its practical applications, the quart also serves as a learning tool in culinary education. By mastering quarts and other units of measurement, students develop the skills needed to succeed in the culinary arts, ensuring that they can create delicious and consistent dishes.
Quart in Scientific Research
In scientific research, precise measurement is paramount, and understanding how much is a quart can be crucial in various scientific disciplines. While the metric system is predominantly used in science due to its standardized nature, the quart still appears in specific contexts, particularly in the United States.
In laboratories, the quart may be used to measure liquids for experiments, especially when working with chemicals, solutions, or biological samples. Accurate measurement of these substances is essential for ensuring the validity and reproducibility of scientific results. Researchers must be adept at converting quarts to metric units like liters and milliliters to maintain consistency in their work.
The quart is also relevant in environmental science, where it may be used to measure water samples, pollutants, or other substances. Understanding how much is a quart allows scientists to accurately assess environmental data, contributing to research on water quality, pollution, and ecosystem health.
In agricultural research, the quart is used to measure dry ingredients like seeds, feed, or soil samples. Accurate measurement is essential for studying crop yields, soil health, and agricultural sustainability. Researchers working in these fields must be familiar with quarts and their conversions to other units to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their findings.
While the quart may not be the primary unit of measurement in scientific research, its importance in specific contexts cannot be understated. By understanding how much is a quart and its role in scientific disciplines, researchers can ensure that their work remains precise and credible.
Quart in International Trade
International trade relies heavily on standardized measurements to ensure fair and accurate transactions. Understanding how much is a quart is essential for businesses and individuals involved in the trade of goods, particularly those dealing with liquids and dry commodities.
The quart is commonly used in trade agreements and contracts, especially in industries like agriculture, food and beverage, and manufacturing. Accurate measurement of products like milk, oil, grains, and other commodities is vital for determining pricing, logistics, and quality control. Ensuring that all parties have a common understanding of how much is a quart can prevent disputes and facilitate smooth transactions.
In international contexts, the difference between the US and UK quarts can be a source of confusion. Businesses must be aware of these differences and ensure that all measurements are clearly defined and understood. This awareness helps prevent costly errors and misunderstandings, ultimately supporting successful and profitable trade relationships.
In addition to its practical applications, understanding how much is a quart in international trade also fosters cross-cultural communication and collaboration. By recognizing the diversity of measurement systems and their historical contexts, businesses can build stronger connections with partners and clients from around the world.
As globalization continues to shape the world economy, understanding the quart and its role in international trade remains a valuable skill. By mastering this unit of measurement, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of global commerce, ensuring that they remain competitive and successful in an ever-evolving market.
Common Misconceptions About Quarts
Despite its widespread use, the quart is often misunderstood, leading to common misconceptions and mistakes. Understanding these misconceptions can help clarify how much is a quart and ensure accurate measurement in various contexts.
One common misconception is that the quart is the same in both the US and UK systems. As we have discussed, the US quart is smaller than the UK imperial quart, leading to potential confusion, especially in international contexts. It's crucial to specify which system is being used when discussing quarts to avoid errors in measurement.
Another misconception is that quarts are only used for measuring liquids. While quarts are often associated with liquid measurement, they are also used for dry ingredients in the US customary system. This versatility makes the quart a valuable unit in both cooking and scientific research, where accurate measurement of dry and liquid substances is crucial.
Some people may also mistakenly believe that quarts are interchangeable with metric units like liters. While there are approximate conversions between quarts and liters, they are not equivalent. Accurate conversion requires understanding the specific values associated with each unit and using conversion factors or tools.
Finally, a common misconception is that quarts are outdated and rarely used. While it's true that the metric system is more widely adopted globally, the quart remains a relevant and important unit of measurement in many countries, particularly in the United States. Understanding how much is a quart and its role in various systems and contexts is essential for accurate measurement and communication.
Tools for Measuring Quarts
Accurate measurement of quarts requires the right tools and techniques. Understanding how much is a quart and using appropriate measurement equipment ensures precision in cooking, scientific research, and other applications.
For liquid measurements, graduated measuring cups are the most common tool. These cups are typically marked with both US customary and metric units, allowing for easy conversion between quarts, cups, and liters. Using a clear, marked measuring cup ensures that liquids are measured accurately, reducing the risk of errors in recipes or experiments.
When measuring dry ingredients, it's important to use a dry measuring cup or container. These tools are designed to hold a specific volume of dry goods and allow for precise measurement by leveling off the top. Ensuring that dry ingredients are accurately measured is crucial, particularly in baking and scientific research.
For larger quantities, graduated cylinders or beakers may be used, especially in scientific research. These tools provide accurate measurement of both liquids and dry substances, making them versatile and essential in laboratory settings.
In addition to physical tools, digital measurement devices and online converters can also be valuable resources. Digital scales and measuring devices offer precise measurements, often with the ability to switch between different units. Online converters provide quick and easy conversions between quarts and other units, ensuring accuracy and convenience.
By using the right tools and techniques for measuring quarts, you can ensure precision and accuracy in your work, whether in the kitchen, laboratory, or marketplace.
The Future of the Quart
As measurement systems continue to evolve, the future of the quart is a topic of interest and speculation. While the metric system is increasingly adopted worldwide, the quart remains relevant in certain regions and industries, raising questions about its future role.
In the United States, the quart is likely to remain a staple of the customary system, particularly in everyday life and culinary contexts. The continued use of the quart reflects not only tradition but also the practical needs of individuals and industries that rely on this unit for accurate measurement.
Globally, the metric system's dominance may lead to a gradual decline in the use of quarts, particularly in scientific and international contexts. However, the quart's historical significance and continued relevance in specific areas suggest that it will not disappear entirely.
As technology advances, digital measurement tools and online resources may bridge the gap between different measurement systems. These innovations could make it easier to convert between quarts and other units, ensuring that individuals and businesses can navigate a world where multiple standards coexist.
Ultimately, the future of the quart will depend on the balance between tradition and innovation. As societies continue to evolve and adapt, the quart may find new applications and contexts, ensuring its place in the ever-changing landscape of measurement systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much is a quart in liters?
In the US customary system, one quart is approximately 0.946 liters. In the British Imperial system, one quart is approximately 1.136 liters.
2. How many cups are in a quart?
In the US customary system, there are 4 cups in a quart. In the British Imperial system, there are 4 imperial cups in a quart.
3. What is the difference between a liquid quart and a dry quart?
A liquid quart is used to measure liquids and is equivalent to 32 US fluid ounces. A dry quart is used for dry ingredients and is equivalent to 67.2 cubic inches.
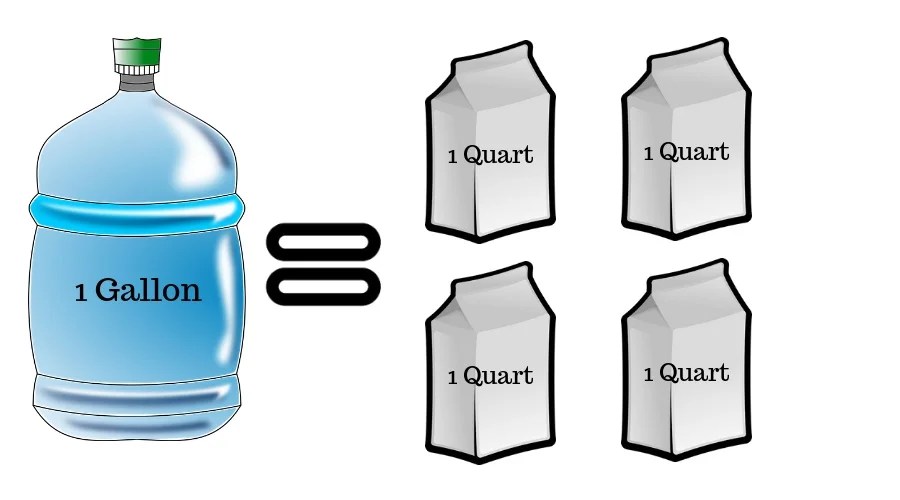
4. How does a quart compare to a gallon?
In both the US customary and British Imperial systems, a quart is one-fourth of a gallon. Therefore, there are 4 quarts in a gallon.
5. Can I use quarts in scientific measurements?
While the metric system is more common in scientific research, quarts may still be used in specific contexts, particularly in the United States. It's important to convert quarts to metric units for consistency in scientific work.
6. Are quarts still relevant in modern measurement systems?
Yes, quarts remain relevant in the US customary system and in specific industries and contexts. While the metric system is more widely adopted, the quart continues to be used in everyday life and certain professional fields.
Conclusion
Understanding how much is a quart is essential for accurately measuring and communicating volumes in various contexts. From its historical origins to its modern applications, the quart plays a vital role in cooking, scientific research, international trade, and more. By mastering the quart and its conversions to other units, individuals and businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of measurement systems. As the world continues to evolve, the quart remains a relevant and valuable unit, bridging tradition and innovation in the pursuit of precision and understanding.
Article Recommendations
- Coffee Flights Near Me
- Opa Opa Brewing Co
- United States Department Of Health And Human Services
- Nyc Department Of Corrections
- Varsity National Yearbook Weeek
- Maid Of The Mist Niagara Falls
- Victoria Braswell The Teacher
- Maid Of The Mist Niagara Falls
- Iglesia De Jesucristo De Los Santos De Los Ultimos Dias
- What East Jackson Volleyballs Look Like